Vyvanse was the tenth most commonly prescribed drug in the United States of America in 2014, according to a survey by IMS Health Market Research Company (USA).
With over 10 million prescriptions written each year, the stimulant Vyvanse ranks No. 5 among the most widely prescribed medications in the US, according to a CNN report.
Vyvanse is a stimulant that can cause addictive tendencies in some patients. Similarly, ingredients in the Vyvanse deposited in the cells of your system can cause a few adverse effects on your health.
Before you use this drug, it is good to know how long Vyvanse stays in your system.
In this article, let us see how long Vyvanse residues and their metabolites, including blood, urine, hair, and saliva, can stay in your system.
What is Vyvanse?
Vyvanse, also known as Lisdexamfetamine, is a psychostimulant medication.
It is used to control, improve, and prevent syndromes such as ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) and overeating.
Lisdexamfetamine is the chief compound contained in Vyvanse.
Vyvanse is effective for treating ADHD in children aged 6 and older. In the priority approval program, the FDA has approved it.
In the case of treating “Binge Eating Disorder” (BED), it is prescribed for people over 18 years old. However, it is not at all a medicine for obesity or weight loss, despite its effectiveness in managing binge eating disorders.
This drug is available in tablets, capsules, liquid, and bandages.
Do not take Lisdexamfetamine for a longer period than your doctor has prescribed. Abuse or overuse of this medication can lead to drug dependence or addiction.
Vyvanse does not contain an active amphetamine, unlike other popular ADHD medicines like Ritalin and Adderall.
Before we discuss how long Vyvanse can stay in your body (blood, urine, or saliva), let us explore a few more essential facts about this drug.
How Does Vyvanse Work?
Lisdexamfetamine, contained in this drug, is composed of two other compounds, dextroamphetamine, and lysine. This compound in Vyvanse remains inactive. However, once activated within the body, they help increase the concentration of dopamine and epinephrine in your body.
The brain releases epinephrine and dopamine neurotransmitters that cause an increase in neurophysiological arousal. Thus, ADHD is treated in your system.
Vyvanse improves your mood and increases concentration. This drug gives quick relief from depression and anxiety.
Because of its mood-enhancing effect, some patients may develop a dependency on this pill.
How Does Vyvanse Affect the Brain and Body?
It is good to know how Vyvanse affects the brain and body and how long the effects last.
Vyvanse is an amphetamine that helps to balance the dopamine and norepinephrine chemical substances in the brain. This drug increases the production and release of dopamine, promoting a feeling of pleasure and relaxation. It relieves the symptoms of ADHD and reduces hyperactivity and impulsivity.
Lisdexamfetamine induces strong feelings of motivation, concentration, self-confidence, and euphoria.
However, an overdose of this drug produces countereffects like increased irritability, anxiety, and sleep disorders. Abuse of Vyvanse can cause hallucinations, panic attacks, paranoia, and delusions.
How long do the effects of Vyvanse last in your brain?
After you have stopped using the drug, the effects created on your brain continue to last for 3 days at a diminishing rate.
What is the half-life of Vyvanse?
The ‘half-life of a drug’ refers to the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the body to reduce by half.
In most cases, five half-lives are required to detoxify or eliminate a drug from your system fully.
Vyvanse’s half-life is very short, unlike many other drugs, which have a half-life span of up to 48 hours. In less than one hour, Vyvanse reaches its half-life in your system.
Half the dose of Vyvanse disappears from your system within 1 hour after consuming it.
According to some scientific estimates, in less than 5 hours, 95 percent of Vyvanse will be eliminated from your system. However, its metabolites continue to stay in your system for some time.
How Long Does Vyvanse Stay in Your System?
Any drug a person consumes will stay in the system for some time.
Now, how long does Vyvanse stay in your urine, hair, and blood? Does Lisdexamfetamine stay in the system even after stopping the drug intake?
A drug test can detect the presence of Vyvanse in your system, including the metabolites left behind by it.
Each drug influences the system differently, and no common rule defines how long each drug stays in your system.
A few conditions determine the partial retention of a drug in the system for a period of time.
One of the key factors that influence drug retention in the system is the food you consume. The quantity and types of foods you consume can alter the absorption level of the drug.
For example, Vyvanse is quickly absorbed by the body when it is taken one hour before a meal. In such a scenario, the retention of this drug in the stomach may last for less than 30 minutes.
Whereas, when Vyvanse is taken during or after a meal, the absorption of this drug by the body takes a long time—up to 4 hours.
According to some of the tests, after every 12 hours, the average amount of Vyvanse in the body is reduced by half. By this estimate, Vyvanse will not be potentially present in your system after 36 hours of consuming it.
Most parts of Vyvanse get eliminated from your body through excretion. It is difficult to trace out Lisdexamfetamine in your body after 8 hours of ingesting it.
Some tests have shown that 50 percent of Vyvanse will be eliminated from your system within 1 hour after ingesting it.
However, the metabolites of this drug can be traced in your system for much longer.
The enzymes in the red blood cells metabolize Lisdexamfetamine into two compounds, namely dextroamphetamine, and lysine. These two compounds are the metabolites of Vyvanse that will stay in your system for a longer time.
Tests for Tracing Vyvanse in Your System
A drug test involves technical analysis of a biological specimen, such as blood, urine, saliva, hair, breath, sweat, etc.
Let us now look at the biological specimen tests usually performed for ascertaining the presence of Lisdexamfetamine in the system.
Blood Test
A blood test is not a preferred test for detecting the existence of Vyvanse in your body. A blood test cannot detect Lisdexamfetamine after 8 hours of ingesting the pill.
Similarly, the compounds dextroamphetamine and lysine can be detected in the blood only if the test is done within 24 hours of taking the drug.
Urine Test
A urine test is considered the best biological specimen test for discovering the presence of Vyvanse in your system.
A urinalysis test can indicate the presence of Vyvanse metabolites in the urine sample.
However, urine’s acidity level, or pH value, affects the test’s positive or negative outcome.
A urine test can detect the presence of Lisdexamfetamine metabolites up to 3 days after the last use of the drug.
Saliva Test
A saliva test is better than a blood test for detecting Vyvanse in your body. Testing your saliva can detect dextroamphetamine and lysine compounds in your system for up to 48 hours.
The high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) technique is used for this test. Using this method, the metabolites present in saliva can be detected in less than 16 minutes.
Hair Test
A hair test for detecting the presence of a drug is a complicated process. This test is rarely done.
Usually, the metabolites of a drug deposited in the hair follicles can be detected for up to 90 days.
The drug metabolites deposited in the hair follicles do not impact your system.
The technique of mass spectrometry or gas chromatography is used for analyzing the hair follicle.
However, it is difficult to detect the presence of Vyvanse in the hair follicles if you have very high levels of melanin pigment in the body.
This test can be done at least one week after consuming the drug.
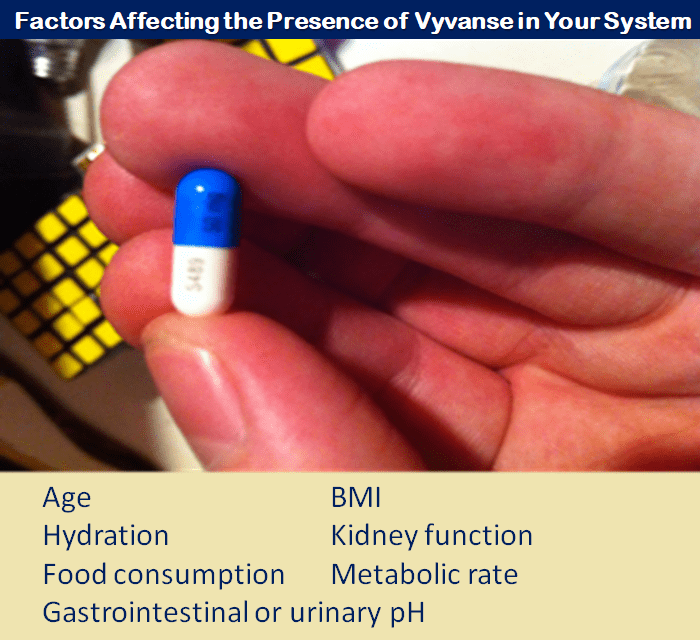
Factors Influencing the Retention of Vyvanse
Few factors determine the retention of a drug in the system for a period.
Each individual has varying health conditions crucial to the absorption and retention of a drug in the body.
Individual factors that determine the effect of a drug on the body are:
- Age
- BMI
- Hydration
- Kidney function
- Food consumption
- Metabolic rate
- Gastrointestinal or urinary pH
Older adults take longer to eliminate drugs like Vyvanse from their systems because of poor renal and liver function.
Similarly, people with poor BMI scores or obesity issues will retain the residues of Vyvanse in their bodies for longer.
Persons who have been taking Vyvanse regularly for a considerably long period will retain the properties of this drug for a longer duration.
Consuming a higher dose of the drug will extend the elimination period of the medication from your body.
A person with a well-hydrated body will excrete the properties of the drug from the system at a faster rate.
An individual with healthy liver and kidney function enjoys faster absorption and elimination of the drug from the body.
How to Clear Vyvanse from Your System?
You can expedite the elimination of Vyvanse from your body by adopting a few remedial steps.
Stop Using
Completely stop the usage of Vyvanse if you want to eliminate its properties from your system.
However, if you have not completed the medication prescribed by your doctor, do not stop it abruptly without consulting the doctor.
Acidifying Urinary pH
One of the fastest ways to eliminate any drug from your system is by acidifying your urinary pH. It drastically reduces the half-life of the metabolites of the drug.
It is possible to eliminate 90 percent of Vyvanse from your system in less than three days by using this method.
You can decrease the pH factor in urine by correcting your diet, taking betaine supplements, or drinking soda in moderation.
Increase Urinary Flow
Vyvanse is ultimately eliminated from the system via urine.
Drinking more water and taking liquid foods can increase the frequency of urinary flow for the faster excretion of metabolites of this drug.
Final Thought
How long Vyvanse stays in your system largely depends on the dosage and frequency of using this drug.
Age, health conditions, the cross effects of other drugs, pH levels in the urine, and the individual’s metabolic rate are other key factors that determine the retention period of a drug in the system.
On average, 90 percent of the Vyvanse metabolites are excreted within three days after you stop taking this drug.
Your system will be free of Vyvanse within 7 days of consuming it. However, an insignificant number of metabolites of this drug can stay in your hair follicle for up to 90 days. The drug metabolites deposited in the hair follicles do not affect your health.
Read next: