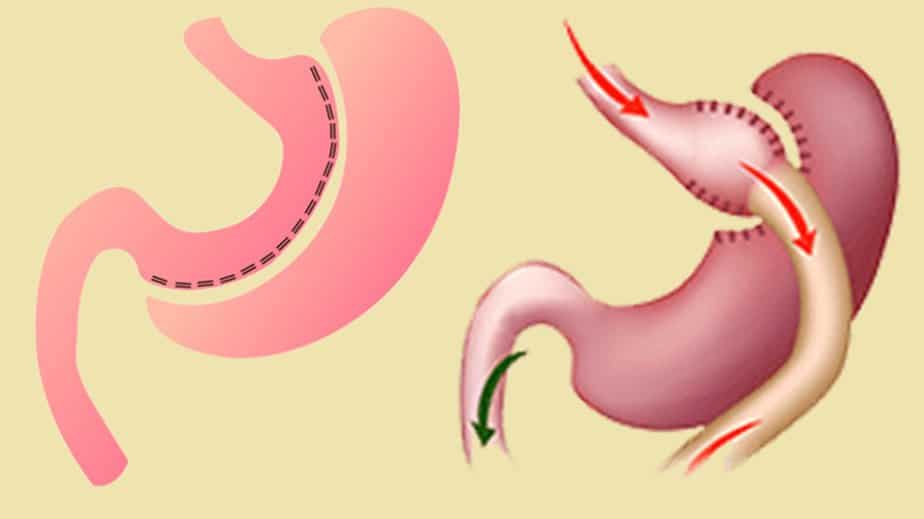
Sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass are the most popular bariatric surgeries.
Surgery is the last resort for people who have tried everything else to lose weight, like diets, supplements, and exercise but haven’t seen the results they want.
If all your efforts to lose weight have gone in vain, you should consider undergoing a vertical sleeve gastrectomy or Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Morbid obesity is dangerous because it can lead to fatal diseases such as type 2 diabetes, stroke, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. It is preferable to have metabolic and bariatric surgery than to become a victim of the deadly illnesses that morbidly obese people are prone to.
This article will talk about the differences between gastric bypass and gastric sleeve surgeries, including their benefits, and drawbacks.
Difference Between Gastric Sleeve and Gastric Bypass Procedure
Bariatric surgery is a procedure that can be performed laparoscopically or as open surgery by a bariatric surgeon.
Vertical sleeve gastrectomy (VSG), also called gastric sleeve, is the best option for people who are very sick or aren’t physically fit enough to have more invasive weight loss surgeries.
VSG surgery can be done on its own, or in some cases, doctors will do this first, and then, after a few months, do a full gastric bypass if the patient hasn’t lost enough weight.
Gastric bypass involves a lot more invasive procedures. After this surgery, the stomach was reduced to the size of a small pocket.
The doctors use a laparoscope (a narrow tube equipped with a camera and light) to perform both surgeries. A few small cuts are made in the stomach so that the laparoscope and other small tools can be put into the abdomen, and the stomach and intestinal bypass can be adjusted.
In gastric bypass, the stomach is divided into two parts. A small pouch is created in the upper part of the stomach. A new pathway is produced by cutting through the middle of the small intestine and connecting it to the stomach pouch. A bypass of the lower part of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine is created in this procedure.
Gastric bypass (GBS) shortens the digestive tract, drastically reducing the quantity of food you can eat.
It will take about 2 hours to complete the GBS procedure, and the patient will require about 2 to 3 months to return to normal health.
The gastric sleeve procedure involves the removal of three-quarters of the stomach. The stomach size is drastically reduced and takes the shape of a sleeve or tube.
The VSG does not change the gastrointestinal path. The food goes through the entire digestive tract. Usually, this surgery will take about 2 hours to perform and about 2 months to heal the internal wounds fully.

Differences In Results
Gastric sleeve patients lose weight gradually over time by reducing the amount of food consumed at one time because of the smaller stomach. The side part of the stomach (3/4) is fully removed. In VSG, only a small tube-like portion at the top of the stomach is left with little capacity for storing food.
In a vertical sleeve, no intestinal bypass is made, but the ghrelin hormone gland, which helps the brain make you feel hungry, may be removed.
Patients with VSG lose up to 70% of their total body weight in 6 months to 2 years because they can’t eat as much.
Gastric bypass patients achieve much more profound weight-loss results. In GBS, not only are the major portions of the stomach closed but the food is also made to bypass the major portions of the small intestine.
A pouch created at the upper part of the stomach can hold only a small amount of food at a time. This causes the person to feel full despite the small amount of food consumed. As the bypass shortens the digestive tract, the body does not absorb extra calories and fat.
Gastric bypass patients lose weight much faster and more effectively than those who undergo the vertical sleeve, but it can cause a few health problems in some people.
How Are The Patients Selected?
Weight-loss surgery is typically performed on obese patients with a BMI greater than 40. However, bariatric surgery could be performed on a person with a BMI score as low as 30 if the patient suffers from diabetes mellitus, infertility, and high blood pressure due to obesity-related conditions.
Doctors usually recommend one of these surgeries based on the patient’s specific obesity and needs.
The actual sleeve is intended not only to reduce body weight but also to treat other obesity-related diseases.
In some cases, the desired weight loss results are not obtained from the first surgery. Patients who undergo GSV surgery or a duodenal switch could be recommended to undergo the GBS surgery after a few months or a year.
Gastric bypass is suitable for patients with a BMI score above 40. It is normally required for people who cannot reduce weight with exercise, diet, or medication. This surgery may also be recommended for people suffering from life-threatening obesity-related diseases, but not for those with weak health.
The most effective bariatric surgery is the Roux-en-Y laparoscopic bypass surgery because it yields long-term weight loss. However, the most invasive weight loss surgery can lead to health complications in some patients.
Advantages of Gastric Bypass and Gastric Sleeve Surgeries
Both of the surgeries in the discussion have advantages and disadvantages.
Major benefits of gastric bypass include:
- Most effective weight loss surgery, as it can help reduce up to 80% of excess body weight,
- The food intake drops significantly as the stomach shrinks to a small pouch,
- It is effective for long-term weight loss results,
- It is possible to undo the surgery and get the stomach and the rest of the digestive tract back to how they were before,
- Restricted absorption of calories and nutrients promotes higher weight loss.
Chief advantages of vertical sleeve gastrectomy include:
- This effectively reduces up to 60% of the excess body weight.
- It is a less complicated process than bypass surgery.
- It suppresses appetite as the ghrelin hormone gland is removed through this surgery.
- VSG reduces food intake as stomach size is reduced to the length of a sleeve or tube.
- Unlike gastric bypass, it does not decrease the absorption of nutrients and vitamins, as no bypass is created, and foods get digested, as happens in a healthy person.
- It keeps the small intestine and pyloric valve intact.
- This surgery is good for people with a high BMI score above 50 or patients with Crohn’s disease, anemia, prior surgery impact, or anti-inflammatory medication.
Side Effects And Drawbacks
Let us look at the risks, complications, and disadvantages of vertical sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Some studies have been conducted to analyze both procedures’ risks and disadvantages. Both of these surgeries are good and have proven weight-loss results.
As a side effect of gastric bypass, in some patients, rapid gastric emptying, also called dumping syndrome, often occurs following surgery on their stomach or esophagus.
There are a few disadvantages associated with both of these surgeries, as reported by various studies conducted.
Drawbacks of gastric bypass
- As the length of the digestive tract gets shorter, nutrients and vitamins also can’t be absorbed. The frequency of defecation is increased (3–5 times a day) due to poor digestion of food.
- It causes “dumping syndrome,” which causes diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort immediately after a meal. It may even cause a fear of eating food, especially in an out-of-home environment.
- The patient must follow a strict diet plan post-surgery and give up many common foods.
- There are possibilities of bleeding, infection, and blood clots post-surgery.
- This method involves a complex, invasive surgical procedure.
- This surgery may cause the development of an ulcer, gallstones, bowel obstruction, and reflux.
Drawbacks of gastric sleeve
- Loss of appetite can make the patient weak by not allowing him to eat sufficiently and frequently.
- This surgery can also cause internal bleeding, infection, and blood clots.
- It can cause stomach leakage along the stapled edge.
- It is irreversible and permanent, unlike the GBS.
Dietary Guidelines Comparison
Both surgeries require the patients to follow a well-planned daily diet.
The patient who underwent a vertical sleeve gastrectomy requires:
- About 700 calories per day during the weight-loss period,
- Diet should include five small meals that are chewed into a pureed consistency,
- Snacking between meals should be avoided,
- Dietary protein and nutrient-rich foods should be included.
The patients who have undergone gastric bypass require:
- Eat 800 calories per day during the weight-loss period
- Take three small meals per day.
- Avoid high-fat and high-carb foods and fibrous, sticky, and dry foods that may cause blockage in the narrow intestinal bypass.
- Tough bread, pasta, nuts, and meat are not suitable for consumption.
- Soft drinks and soda should be strictly avoided to prevent bloating.
Conclusion
Bariatric surgeries have become the assured weight loss solution; more and more people are opting for the same.
Gastric sleeve is gaining popularity as it has fewer health complications than gastric bypass. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy suppresses the appetite and reduces food intake capacity by reducing stomach size. Still, at the same time, it does not affect the digestive process and ensures the body receives all essential vitamins and nutrients.
Gastric bypass is excellent for maximum weight loss results as it not only reduces the food intake capacity of the stomach but also prevents the body from absorbing the excess amount of calories as a bypass is created to shorten the food digestion tract. This surgery’s effects can be reversed to the original status of the stomach and digestive tract after achieving the desired weight loss results.
However, gastric bypass is complex and can have side effects that make the person’s life a bit difficult in the post-surgery period. It also makes it harder for the body to absorb the necessary vitamins and nutrients.
Finally, the weight reduction results from both bariatric surgeries are not permanent; the patients can become obese again several months or years after the surgery with changes in food habits or due to the onset of other diseases.
Recommended reading list: